Building Your Free Cyber Security Home Lab
Embarking on a journey into the
world of cyber security can feel daunting, but it doesn't have to be. One of
the most effective ways to learn is by getting hands-on experience, and there's
no better way to do that than by building your very own cyber security lab at
home – completely free! This isn't just a theoretical exercise; it's a
practical project that will immerse you in the tools and techniques used by
cyber security professionals, whether you aspire to be an ethical hacker or a
security analyst.
This guide is designed to take you
from zero to a functional home lab, regardless of your current technical
expertise. We’ll cover the resources you’ll need, the steps to set up your lab,
and how to start using it to gain valuable cyber security experience. All of
the resources and tools mentioned will be linked in the article's resource
section, ensuring you have everything you need at your fingertips.
Why Build a Home Lab?
Before diving into the how, let’s
explore the "why." For newcomers to the cyber security field, a home
lab is invaluable. The industry generally branches into two main career paths:
- Offensive Security (Ethical Hacking): This path focuses on identifying and exploiting
vulnerabilities in systems to strengthen defenses. It's about thinking
like an attacker to better protect against attacks.
- Defensive Security (Security Operations/SIEM Analyst): This path is all about defending systems and networks,
monitoring for threats, responding to incidents, and implementing security
policies.
Regardless of which path interests
you, a home lab provides crucial hands-on experience with the tools and
techniques used in both disciplines.
The Essential Tools: Free and Accessible
To build our lab, we need specific
hardware and software, all of which are free to use. Here’s what you’ll need:
- Laptop or PC:
Your existing computer can serve as the foundation for your lab. However,
it’s important to ensure that your system meets certain minimum
requirements. Ideally, you should have at least 8 GB of RAM (16GB is
highly recommended for smoother performance), along with at least a 256 GB
hard drive, preferably an SSD for faster loading times. You'll be using
this machine to host your virtualized cyber security lab environment, so
sufficient resources are important.
- Virtualization Software: This is the key to running your lab without affecting
your main operating system. Virtualization software creates a virtual
machine (VM) that functions as a separate computer within your existing
system. Popular options include VMware Workstation and VirtualBox, both of
which are free. For this guide, we’ll use VMware Workstation as our
primary virtualization tool.
- Kali Linux ISO:
Kali Linux is a powerful and pre-configured operating system specifically
designed for penetration testing and security auditing. It comes packed
with a range of security tools, and downloading it as an ISO file allows
us to install it directly into our virtual machine.
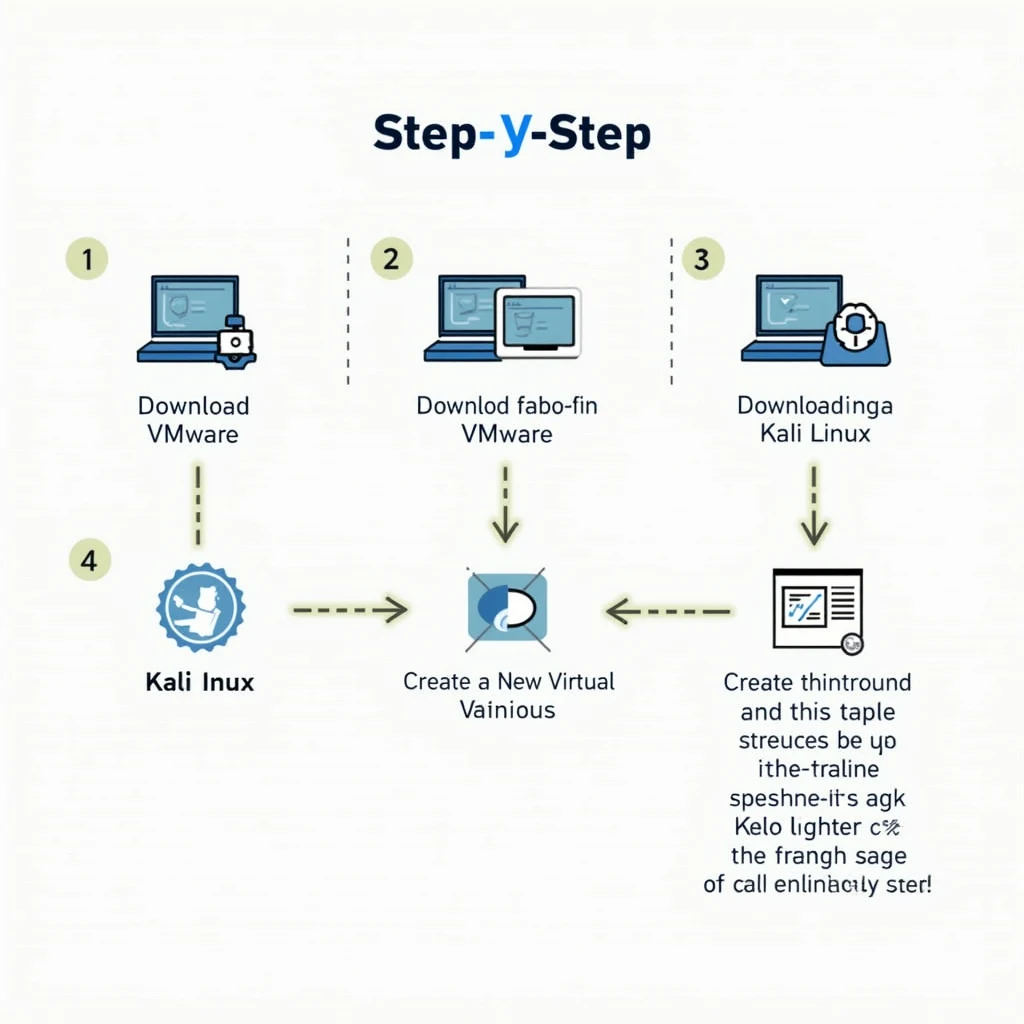
Step-by-Step: Building Your Lab
Let's walk through the setup
process, step-by-step:
- Install VMware Workstation: Download and install VMware Workstation for free from
the official VMware website. Follow the standard installation prompts to
complete the process.
- Download the Kali Linux ISO: Navigate to the official Kali Linux website and
download the latest version of the Kali Linux ISO file. This is the
operating system that will form the core of your lab.
- Create a New Virtual Machine: Open VMware Workstation and create a new virtual
machine. Allocate resources from your existing PC to this virtual
environment. A minimum of 4GB of RAM and 30-40GB of hard drive space is
recommended for the Kali Linux VM.
- Install Kali Linux:
Select the Kali Linux ISO file as the boot disk during the virtual machine
setup. Follow the on-screen instructions to install Kali Linux on the
virtual machine. Be sure to create a secure password and set up your user
account.
- Update Kali Linux: Once Kali Linux is installed, update all of its packages. This ensures that you have the latest versions of all tools and software. Use the following commands in the terminal:
sudo apt update
sudo apt upgrade
- (Optional) Configure an Isolated Lab Network: For those wanting an extra layer of protection, you
can configure an isolated virtual network for your lab. This prevents your
training and testing from inadvertently affecting external devices. This
is not required, and you can skip this step if you primarily just need it
for CTFs and training.
With these steps completed, you have
a barebones cyber security home lab! It's remarkably simple to set up and will
serve as the foundation for all your future training.
The Fun Part: Adding Cyber Security Tools
Now that we have our lab, it's time
to start adding some tools! Kali Linux comes pre-installed with many useful
programs, and you can familiarize yourself with them. However, you'll also want
to add other tools that interest you.
As an example, let's install Burp
Suite, a popular web application security testing tool. To install it, use this
command in your Kali Linux terminal:
sudo apt install burp-suite
You will use the command line
directly when installing tools this way. The command line can be intimidating
for beginners, but it's critical to get comfortable with it. Cyber security
professionals frequently use Linux through the command line and many of the
hacking and CTF tools are built on the command line. Spend a few days
practicing basic Linux commands, such as creating files and folders, navigating
directories, updating packages, and more. Mastering the command line is an
essential step in your cyber security journey.
Training Opportunities: Taking Your Lab to the Next Level
Now that you have a lab, here are
some great ways to begin training:
- Vulnerable Applications: Rather than creating your own target machines, which
can be resource-intensive for beginners, you can utilize existing
vulnerable applications on the internet. Applications like Metasploitable
and OWASP Juice Shop are designed to be exploited, providing real-world
practice without the risk of breaking the law.
- OWASP Top 10:
Focus on the OWASP Top 10, the most common web vulnerabilities. Find
online guides for exploiting vulnerabilities like cross-site scripting
(XSS). This will allow you to understand vulnerabilities and how attackers
exploit them in the real world. Many of these online guides can be easily
found with a simple Google search.
- Capture the Flags (CTFs): CTFs are a fantastic way to learn both offensive and
defensive security. Websites like CTFtime provide lists of upcoming CTFs
which are essentially hacking challenges. They challenge your skills and
are applicable to both red team and blue team skills. A lot of the CTF
challenges are based on real world vulnerabilities.
- IT Fundamentals:
Prior to focusing on cyber security, building a solid foundation in IT is
helpful. Consider taking IT training courses focused on network
administration. These will teach you how to create things like active
directories and ticketing systems that are essential to understanding
larger cyber security ecosystems.
Additional Learning Resources
To further your learning, here are
some additional resources:
- Google Cyber Security Certification: Google provides a cybersecurity certificate with hands
on experience using real tools and methods and should prove beneficial to
all beginners in cyber security.
- Springboard Cyber Security Bootcamp: For a more structured approach, consider a bootcamp
like Springboard, which offers a comprehensive curriculum, mentorship, and
a job guarantee. Using the link provided in the resource section you will
be able to find a code for $1,000 off.
Conclusion: The Start of Your Cyber Security Journey
Starting in cyber security doesn’t
require years of technical expertise. With a bit of dedication, the resources
available and a willingness to learn, you can build your own home lab and begin
training today. This is not a journey that will be easy, and it will take time,
but for those that are patient and willing to learn there is no limit to how
far you can grow.
The path to becoming a cyber
security professional requires a continuous thirst for knowledge and an
interest in the technical intricacies of threats, vulnerabilities, and
exploits. If you’ve made it this far, you've already built a fully functional
cyber security lab, and your journey is just beginning!
Start practicing, studying,
exploring, and most of all, learning! Be sure to let us know about your
progress in the comments below!
VMware Workstation Player (Free): Kali Linux ISO Download: Metasploitable (Downloadable VM): Note: Metasploitable is often provided as a direct download or through third-party mirrors since it's an older VM. You can find it by searching "Metasploitable download" on Google. Be cautious and download from reputable sources. One example link is: https://sourceforge.net/projects/metasploitable/files/Metasploitable2/
OWASP Juice Shop: You can also find the GitHub repo for it here: https://github.com/juice-shop/juice-shop -for installation on your own server
OWASP Top 10: CTFtime: Google Cybersecurity Professional Certificate: Springboard Cybersecurity Bootcamp: - Please note: As a language model, I don't have a specific affiliate link or coupon for Springboard. It's best to visit their official site and check for current promotions or use a search engine to look for Springboard discounts.
Metasploitable: Be careful when downloading Metasploitable, as it's an intentionally vulnerable VM. Download only from trusted sources.Springboard: Always confirm pricing and terms directly with Springboard on their website, as promotions and conditions change frequently.Security: Always practice safe downloading and install software from reputable sources. Double-check any links that seem suspicious.